Understanding Conventional Home Loans: Your Comprehensive Guide
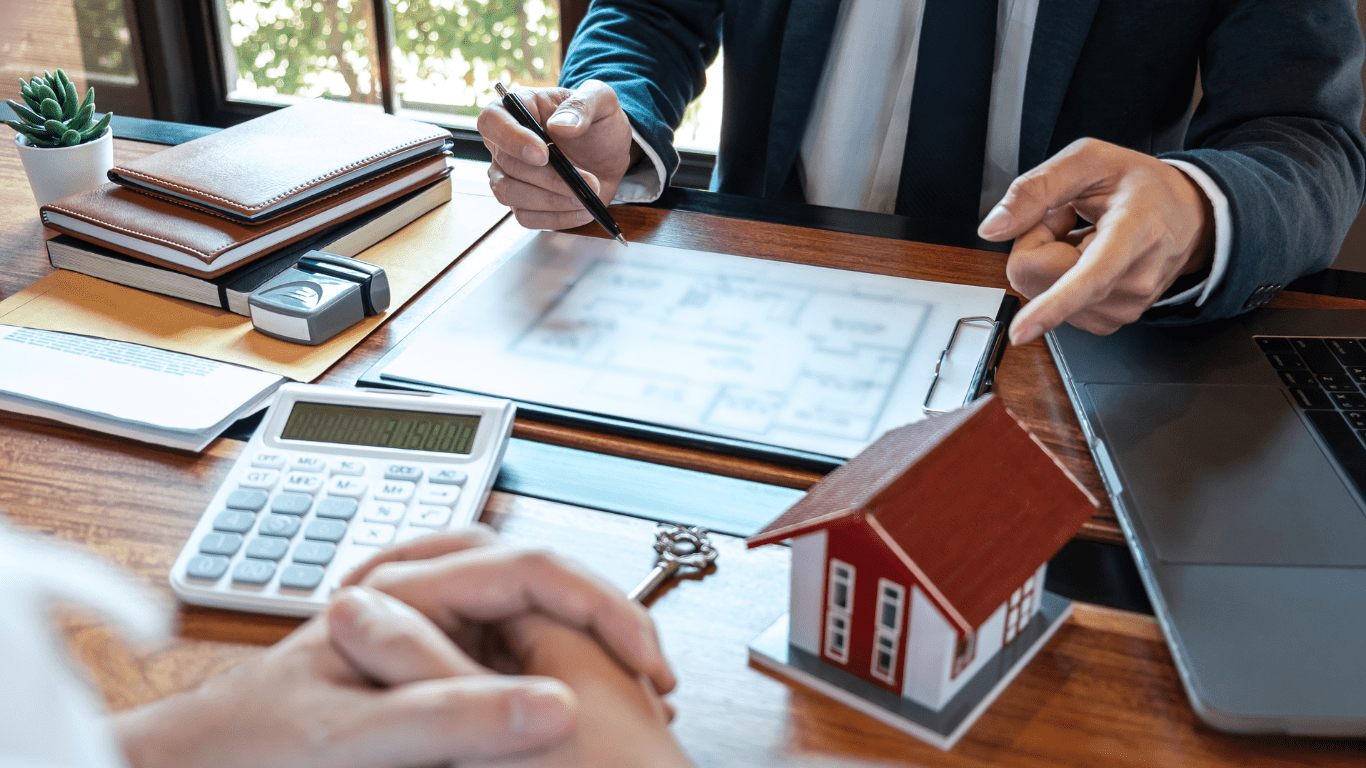
When it comes to buying a home, financing is often a crucial aspect. Among the array of mortgage options available, conventional home loans stand out as a popular choice for many homebuyers. Understanding what these loans entail can empower you in making informed decisions about your homeownership journey.
What Are Conventional Home Loans?
Conventional loans are mortgages not backed or insured by the government, such as the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), or the USDA. Instead, they are backed by private lenders, and their terms and requirements are determined by the lending institution or by standards set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, two government-sponsored enterprises.
Advantages of Conventional Loans:
- Flexibility: Conventional loans offer more flexibility in terms of loan amounts and property types, making them suitable for various homebuyers.
- No Mortgage Insurance Requirement: With a down payment of 20% or more, borrowers can avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI), unlike some government-backed loans.
- Competitive Interest Rates: Interest rates for conventional loans can be competitive, especially for borrowers with strong credit scores.
Eligibility Criteria:applicants
Lenders typically evaluate applicants based on several factors, including credit score, debt-to-income ratio, employment history, and down payment amount. While requirements may vary among lenders, a credit score of 620 or higher is often considered the minimum for conventional loans.
Key Differences from Other Mortgage Options:
- FHA Loans: Government-backed FHA loans often have more lenient credit requirements and allow lower down payments but may have higher upfront and ongoing mortgage insurance costs.
- VA Loans: Exclusively for eligible veterans, active-duty service members, and certain military spouses, VA loans offer benefits such as no down payment and relaxed credit requirements.
- USDA Loans: Aimed at rural and suburban homebuyers, USDA loans offer zero down payment options but are limited to specific geographic areas.
How to Apply for a Conventional Loan:
- Check Your Credit: Review your credit report and work on improving your score if needed.
- Gather Financial Documents: Lenders will require documents like pay stubs, bank statements, and tax returns to assess your financial situation.
- Shop Around for Lenders: Compare offerings from different lenders to find the best rates and terms.
- Get Pre-Approved: Pre-approval helps determine how much you can borrow and strengthens your position when making an offer on a home.
General FAQs
1. What exactly is a conventional home loan?
Conventional home loans are mortgages that aren’t backed by the government (like FHA, VA, or USDA loans). Instead, they’re supported by private lenders or government-sponsored entities like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
2. How do conventional loans differ from government-backed loans?
Unlike government-backed loans, conventional loans don’t have government insurance or guarantee. They often have stricter requirements but may offer more flexibility in terms of loan amounts and property types.
3. What are the advantages of choosing a conventional loan?
Some advantages include:
- Flexibility in loan amounts and property types.
- Avoidance of mortgage insurance with a 20% or more down payment.
- Competitive interest rates, especially for borrowers with good credit scores.
4. What credit score do I need for a conventional loan?
While requirements vary among lenders, a credit score of 620 or higher is often considered the minimum for conventional loans. However, higher credit scores generally result in better interest rates.
5. How much down payment is required for a conventional loan?
Conventional loans often require a down payment ranging from 3% to 20% of the home’s purchase price. Avoiding private mortgage insurance typically requires a 20% down payment.
6. Can I use a conventional loan for different types of properties?
Yes, conventional loans can be used for various property types, including primary residences, secondary homes, and investment properties.
7. What documents do I need to apply for a conventional loan?
Lenders typically require documents such as pay stubs, bank statements, tax returns, and proof of assets to evaluate your financial situation.
8. Are there limits on how much I can borrow with a conventional loan?
Yes, conventional loans often have maximum loan limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which may vary depending on the area’s housing market.
9. How long does it take to get approval for a conventional loan?
The approval process varies, but it typically takes a few weeks from application to approval, depending on factors like the lender’s workload, documentation completeness, and property appraisal.
10. Can I refinance with a conventional loan?
Yes, you can refinance with a conventional loan to adjust your interest rate, change the loan term, or take cash out of your home equity, depending on your financial goals and eligibility.7